Digital Marketing
Building Scalable Fintech Apps Using Microservices Architecture
Published
4 months agoon
By
Engrnewswire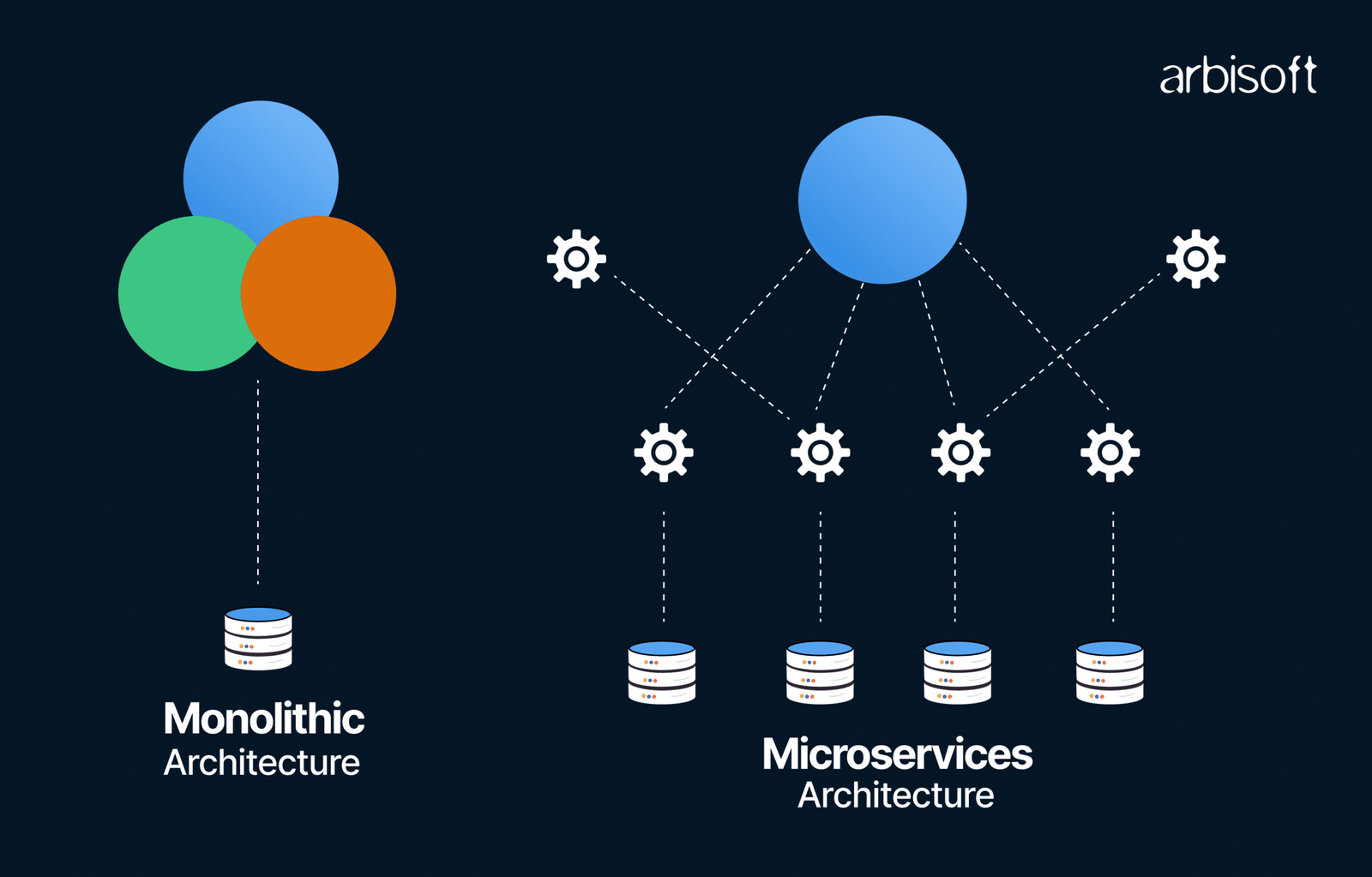
Building a fintech app that keeps up with growing users can feel like chasing your own tail. Slow loading times or system crashes frustrate customers and hurt trust. You need a solution that manages growth effortlessly.
Microservices architecture might be the answer you’re looking for. Big names in finance, like PayPal, use this approach to build faster, more resilient systems. It breaks apps into small parts, which work independently but connect seamlessly.
This blog will guide you on how microservices address common app challenges. You’ll discover tools and tips to accelerate development and enhance reliability. Stay tuned; it’s worth it!
Key Principles of Microservices Architecture in Fintech
Developers break applications into small, independent services for better flexibility. Each microservice focuses on a single task, making updates faster and more efficient.
Service-oriented design
Service-oriented design separates applications into smaller, specialized services. Each service addresses one distinct function, such as processing payments or verifying user accounts in digital banking solutions.
This modular method simplifies updates and enables teams to focus on different components without causing interference.
‘A successful microservices strategy starts with designing for independence,’ says software architect Sam Newman.
By organizing fintech apps in this manner, developers build systems that expand smoothly as business needs grow. Teams also sidestep the challenges of tightly integrated monolithic apps that often struggle under heavy traffic in financial technology platforms.
Independent deployment and modularity
Independent deployment allows developers to update one microservice without affecting others. This decreases downtime and prevents service interruptions for end users, an essential aspect in financial technology applications.
For example, if a digital banking feature requires an upgrade, it won’t interfere with trading or payment services operating simultaneously.
Modularity ensures each service concentrates on a specific function like payments processing, account management, or fraud detection. Teams can build and maintain these components independently while still integrating efficiently into the larger app structure.
This arrangement simplifies troubleshooting and allows for quicker updates across distributed systems.
Benefits of Using Microservices for Fintech Apps
Microservices make building financial apps faster and more effective. They allow developers to create small, focused services that manage specific tasks.
Enhanced scalability
Breaking down applications into smaller, independent services allows fintech apps to handle growing demands effortlessly. Each microservice operates separately, letting developers allocate resources based on usage patterns.
Cloud computing further supports growth by providing flexible server capacity. For example, digital banking solutions can scale up during peak trading hours—when traders rely on fast-moving indicators like stochastic crossover and reduce costs during downtime.
Faster development and deployment
Developers create and release fintech apps more quickly using microservices. This architecture divides applications into smaller, independent services. Teams work on different parts at the same time without waiting for others to complete their tasks.
“Speed is the currency of modern software development.”
Containerization tools like Docker make testing and packaging easier. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines automate code updates. These practices minimize delays and keep financial technology solutions competitive in a rapidly evolving industry.
Improved fault tolerance
Microservices architecture enhances fault tolerance by separating failures. If one service in a fintech app crashes, it does not impact the entire system. Other services keep functioning independently, minimizing downtime and the chance of a complete failure.
This distributed systems method avoids bottlenecks during heavy traffic or unforeseen problems. For example, digital banking solutions managing millions of transactions daily benefit from this robust design.
Even under pressure, the structure sustains performance without interrupting user experience.
Core Technologies for Building Scalable Fintech Apps
Building modern fintech apps requires smart tools and careful strategies. Choose the right technologies to meet business goals and handle future growth effortlessly.
API Gateway for seamless integration
An API gateway serves as the primary point for managing communication between microservices and external systems. It simplifies the way fintech apps process multiple requests, ensuring efficient data flow between services.
Instead of directing calls to every service individually, the gateway organizes all traffic effectively.
This tool manages tasks such as authentication, request routing, and rate limiting. For financial technology apps, this is essential for safeguarding sensitive user data and maintaining consistent performance during high demand.
APIs also allow for integrating new features without disrupting existing operations or overloading other services in your app’s environment.
Cloud computing and containerization
Cloud computing enables fintech apps to expand rapidly without hardware constraints. It provides on-demand resources, allowing better management of fluctuating user demands during peak trading hours.
Services like AWS or Microsoft Azure host applications securely while reducing infrastructure costs.
Containerization simplifies app development and rollout by packaging code and dependencies together. Tools like Docker create isolated environments, ensuring consistency across systems.
This method minimizes the risks of errors when transitioning an app from testing to production environments in the financial technology sector.
Event-driven architecture for real-time processing
Event-driven architecture responds to events as they happen. It handles transactions, notifications, or updates immediately when the system receives them. This method enables financial applications to deliver immediate insights and informed actions for users.
For instance, payment processing services can promptly verify and approve transactions. Traders can get market updates without delays, allowing faster decisions. By relying on distributed systems and message brokers like Kafka or RabbitMQ, fintech apps sustain performance during high traffic periods while managing intricate workflows efficiently.
Best Practices for Implementation
Follow flexible development methods, automate repetitive tasks, and embrace collaboration to build fintech apps that handle growth with ease.
Agile development and DevOps integration
Teams in financial technology can accelerate their software development lifecycle with Agile practices. Agile divides projects into smaller parts, allowing frequent updates and testing.
This approach reduces delays and decreases risks during app creation.
DevOps connects developers and operations teams. Through automation tools like CI/CD pipelines, DevOps simplifies processes from coding to production. It fosters collaboration, cuts down bugs, and provides digital banking solutions more quickly to users.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines
CI/CD pipelines automate the software development lifecycle. They allow fintech apps to receive updates more quickly without interruptions or errors. Developers write code, test it immediately, and push changes smoothly into production environments.
These pipelines enhance efficiency in application growth by identifying bugs early. With each small update tested automatically, digital banking solutions remain secure and dependable.
Cloud computing tools like Jenkins or GitLab help simplify this process for distributed systems in financial technology.
Addressing Challenges in Microservices Adoption
Tackling microservices challenges demands smart strategies and a sharp focus on potential pitfalls to keep systems running smoothly.
Managing data consistency
Data inconsistencies can create significant challenges in fintech apps. Microservices complicate this further by managing data across multiple services, which adds to the complexity.
Through distributed systems, developers depend on methods like event-driven architecture and database partitioning to tackle this issue.
Tools like Apache Kafka aid in coordinating data flow between microservices. Establishing a robust API management approach ensures accurate communication while keeping transactions organized.
Approaches such as eventual consistency help maintain system functionality without straining resources.
Ensuring robust security measures
Protecting financial technology apps requires constant vigilance. Developers must implement strong encryption protocols to secure user data during transmission and storage. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of protection for account access, reducing risks from password breaches.
Regular penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities in distributed systems before attackers exploit them. Using API gateways with rate-limiting features prevents abuse and unauthorized access to services.
Cloud-native applications should also incorporate security patches promptly to address emerging threats.
Conclusion
Building fintech apps with microservices creates a strong basis for growth. This process breaks complex systems into manageable pieces, keeping things adaptable and efficient. Developers can respond swiftly to market demands while maintaining reliability.
By adopting this approach, teams gain resources to address challenges with confidence. The future of digital banking relies on intelligent architecture like this.
You may like


Accounting and Payroll Software for UK Small Businesses: A Practical Guide

Vietnam’s Rising Position on the Global Technology Map

The Ultimate Guide to Expert Car Detailing with Jim’s Car Detailing

Why Effective Data Management is Key to Business Success

2026 Guide to Renting in Worthing: Is It Affordable & Livable Compared to the South East?

Top Tips to Find the Best Fridges for Sale at Sydney Wide Discounts

Why Hiring a Property Lawyer in Sydney is Essential for Your Real Estate Success

AI Consulting: A Suitable Guide to Transform Your Business in the UK

What’s Changed in the Way People Plan Later in Life

Everyday Signs Your Eyes Are Working Harder Than They Should

Revolutionizing Healthcare: The Emergence of AI-Driven Analytics

Carol Kirkwood’s Journey: Her Real Age, Husband, Career, and More

How Machine Learning and AI are Redefining the Future?

Aliza Barber: Meet Lance Barber’s Wife, Age, Life, Profile, Career and Net Worth

Evelyn Melendez: Jordan Knight’s Wife Bio, Marriage, Family, Career and Net Worth

Body Positivity and Bodycon: Embrace Your Shape with Homecoming Dresses

Ilan Tobianah Biography: Family, Marriage, Lifestyle, Career and Net Worth

Who was Alice Marrow? Everything to Know About Ice-T’s and His Mother

King Von’s Autopsy Report: The Truth Behind the Tragic Death

Meet Otelia Cox: The Supportive Wife of Tony Cox – A True Fairy Tale Romance

Accounting and Payroll Software for UK Small Businesses: A Practical Guide

Vietnam’s Rising Position on the Global Technology Map

The Ultimate Guide to Expert Car Detailing with Jim’s Car Detailing

Why Effective Data Management is Key to Business Success

2026 Guide to Renting in Worthing: Is It Affordable & Livable Compared to the South East?

Top Tips to Find the Best Fridges for Sale at Sydney Wide Discounts

Why Hiring a Property Lawyer in Sydney is Essential for Your Real Estate Success

AI Consulting: A Suitable Guide to Transform Your Business in the UK

What’s Changed in the Way People Plan Later in Life

Everyday Signs Your Eyes Are Working Harder Than They Should
Category
Trending
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoRevolutionizing Healthcare: The Emergence of AI-Driven Analytics
-

 News6 months ago
News6 months agoCarol Kirkwood’s Journey: Her Real Age, Husband, Career, and More
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoHow Machine Learning and AI are Redefining the Future?
-

 Celebrity2 years ago
Celebrity2 years agoAliza Barber: Meet Lance Barber’s Wife, Age, Life, Profile, Career and Net Worth
